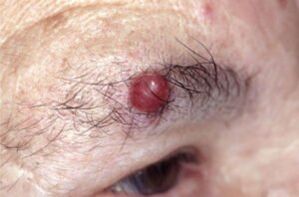
The human papilloma virus (HPV) is located exclusively in the basal layer of the skin, and its reproduction occurs in the upper layers.This disease is characteristic of its chronic form with periodic relapses.
Read more about HPV, its description
HPV is infected with more than half of the world's population.Some of them are simply carriers of the disease, while in others this virus manifests itself as papillomatosis of the skin, mucous membranes.Sometimes this viral disease can be the pathogen of cancer of the cells.HPV is an infection from the Papovaviridea family, which can infect and change epithelial cells.This benign neoplasm is formed in any area of the body:
- neck;
- under the chest;
- on the stomach;
- face;
- on the genitals;
- in axillary hollows;
- on the mucous membranes of the oral, nasal cavities, lips;
- on mucous membranes of internal organs.
This infection belongs to intracellular parasites that are unable to independently reproduce, and use the cells of the human body for this.The virus introduces its DNA in human chromosomes and so it parasitizes for a long time.With a decrease in immunity, you can observe a noticeable activation of this disease.This fact determines the need to treat HPV.The development of this infection occurs in the cells of the body, but it can also exist outside it, but not long.Being in the cells of a living organism, it causes a failure in their division.
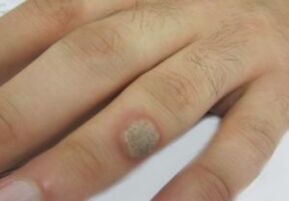
Incubation period and stages of development
The incubation period of the virus is different.This type of virus is characterized by a hidden current.The subclinical form of the course of the disease is characteristic of the appearance of inconspicuous during a simple examination of rashes that cause discomfort to the patient in the genital area.You can immediately become infected with several varieties of papillomaviruses.Under the influence of some factors, the virus is activated and its reproduction begins, and the disease enters the period of clinical manifestations.In 90 % of cases in six months a year, self-healing occurs, in some cases, a chronic recurrent course can occur with a high probability of malignancy (depending on the type of virus).The disease proceeds in four stages (stages):
Stage 1 (initial) - latent course of papillomavirus infection.The virus is in the body, but does not appear, does not cause transformation in cells.At this stage, it can be identified by the analysis of the PCR;
2 - clinical signs arise - in the form of growths on the skin.The virus causes an accelerated division of epidermal cells.At this stage, the virus is detected during PCR, cytology and histology (detected by the presence of hyperkeratosis);
3 - dysplasia.The structure of cells (colocytosis) changes - this is visible under a microscope, since the virus DNA begins to interact with DNA cells and causes the development of the so -called, integrated form.For diagnosis, PCR, cytology and histology methods, as well as colposcopy are used;
Stage 4 - carcinoma.The development of the virus causes the mutation of cells and the occurrence of malignant cells.Invasive cancer is formed.Diagnosis occurs in all of the above methods and on clinical manifestations.
Types of HPV
More than one hundred types of HPV are determined that infect the urogenetal tract of a person that affects the epithelium of the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs - 35 species.For all types of HPV, a classification based on the types of manifesting, rashes and other skin manifestations is used.Tipping HPV with a description looks like this:
- Different types of warts-for their appearance, HPV type 1-5 is responsible;
- Subanary warts (they look like a corn)-1-4 types of HPV.Usually formed in those places where corns or compression occurs.In such places, the skin becomes thicker and when pressing it causes unpleasant sensations.Such warts do not pass themselves and need surgical removal.There are two subspecies of plantar warts.One species sprouts deep into the fabric and hurts a lot, the other type resembles multiple growths, as if glued to each other - this type of warts almost does not bring a feeling of pain
- Flat warts - 3, 5, 10, 28, 49 types.Most often, palms, face are striking.Usually they are found in young people and because of this this type of warts is called youthful.The body often copes with this infection;
- ordinary warts - 27 type of HPV;
- Vulgar warts - type 2 virus (as a rule, the body itself copes with this type of virus).It is transmitted to the domestic way;
- The spicy warts that affects the vagina, vulva, the genitals, the cervix, the uterine, the anus, in men can be on the head of the penis, on the skin of the foreskin, their location in the respiratory tract is also found - types 6, 11, 13, 16.18, 33, 35;
- HPV highly oncogenic risk, causing a precancerous condition - 39 type;
- Founded epidermodisplasia is found.It can be of two types: called HPV 5, 8, 47 - for skin cancer in 9 cases out of 10, this virus is in the patient’s blood, another type caused by HPV 14, 20, 21, 25 usually causes benign neoplasms;
- Laringeal papillomatosis - type 11 virus.Usually transmitted from mother to child, but it is possible to infect with oral sex.Causes difficulties with swallowing, hoarse voice, if the amount of papilloma is large, breathing worsens;
- Bowenoid papulez.This species is provoked 16, sometimes 18, 31-35, 42, 48, 51-54 with the types of HPV.Most often, representatives of the male half that have many sexual partners can occur.Outwardly, these formations look like semicircular or flat growths with a smooth or rough surface, the color is different - from completely light to almost black.The disease can go on its own, it is a neo -info type of virus.
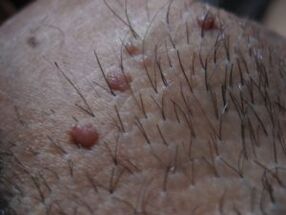
Symptoms and specifics of HPV in men, women and children
In order to overcome the infection in the early stages, human immunity is quite strong.Most often, the disease does not develop and a person does not even suspect the presence of HPV, since external symptoms may not appear.But after some time (months or years), some signs of HPV infection may occur.Statistics indicate only 5-10 % of those who have external symptoms of HPV (Human Papillomavirus).The disease proceeds asymptomatic - the bulk of the sick has no signs of the disease.When activating the virus, growths of various kinds may occur that speak of the presence of various types in the body.Places of localization also speak of the type of virus.For example, papillomas have the form of soft elongated growths (threadless warts) that are attached to the leg, the color may not differ from the color of the skin, but it is also pigmented.Balch -shaped growths may appear, soft to the touch of pinkish color.
In women, the specifics of the course of the disease is such that the development of the disease can occur in a hidden form, but sometimes causes the formation of genital papillomas.Having become infected with the virus, a woman may not observe any symptoms up to the onset of menopause, at this time the virus can provoke the malignant of the cells of the mucous membrane of the genital organs.To prevent the development of cervical cancer caused by the presence of HPV, regular examination by the doctor will help.Since outwardly this disease may not manifest itself.In children, under the influence of the virus, warts on the skin, papillomatosis of the larynx (usually in a chronic return form) can develop.Papillomatosis of the larynx causes breathing problems, up to suffocation syndrome.Skin warts are present in 12 % of schoolchildren, this is the most common dermatological disease in children.

HPV and pregnancy
HPV in a pregnant woman is not the most dangerous disease for herself and the unborn child.The expectant mother should only be wary if she has found 6 or 11 VPV type (causing genital or anal condylomas), which, when transmitted to the newborn, can have consequences in the form of respiratory papillomatosis.In the presence of a condyl in such an amount or places that interfere with the expulsion of the fetus, it is possible to prescribe cesarean, since during ordinary birth, condyloma can provoke the development of bleeding.All other forms of papilloma (non -normatous lesions) are non -hazardous for the child himself and the course of pregnancy.
Diagnostics and to whom you need to contact
The following research methods are used to diagnose papillomavirus:
- personal examination of the patient;
- blood test;
- colposcopy;
- Tsytology smear-papa test;
- Tissue histology;
- PCR is a polymerase chain reaction.This analysis allows not only to learn about the presence of a virus, but also to determine its type.But if the analysis is positive, this does not mean that this type of HPV will not pass on its own.This analysis also determines all types of papillomavirus;
- urethroscopy;
- biopsy.
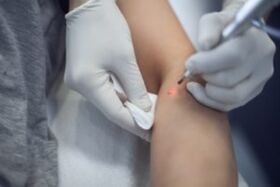
If there are no external signs in the form of a rash, the patient does not have complaints, and the presence of DNA of HPV is determined only by analyzes - it can come from transient viral infection (a person is a carrier).Due to the fact that HPV can be the cause of diseases of different organs, if any, doctors of various directions.In the presence of warts on the skin of the face and body, they turn to a dermatologist.With plantar warts - to a dermatologist or surgeon.With condylomas in men - to the urologist (surgeon), for women - to the gynecologist (surgeon).If condylomas are present in the area of the anus, then you need to contact a proctologist.If a wart epidermodisphelia is suspected, then to a dermatologist or oncologist.Laringeal papillomatosis requires an appeal to an otolaryngologist or surgeon, boenoid papulosis - you need to contact a urologist or venereologist.Differential diagnosis is also required with diseases such as micropapillomatosis, vestibular papillomatosis - they, unlike HPV, do not require treatment, since with the similarity of external signs they are a variant of the anatomical norm.Deciphering the normative values of blood test will be shown by the absence of HPV.
Treatment
So is it completely treated by HPV or not?Today, not a single antiviral drug is known that can remove HPV from the body.Different interferons and other drugs of this series - only reduce existing condylomas, but do not reduce the frequency of new ones.The main method of treatment is the removal of papillomas.The main removal methods are as follows:
- surgical.It is performed under local anesthesia;
- Radio surgical.A tumor is cut off with a radio wave electrode, vessels are coagulated.After an antiseptic bandage is made;
- laser.This method is contactless and bloodless.A crust remains at the place of removal, under it, healing occurs.The disadvantage of the method is the high risk of relapse of the disease, a relatively high price, and the need for grinding the remaining scars;
- Electrocoagulation.According to the results and effectiveness, it is similar to the previous two ways;
- Cryocoagulation.Full removal of papillomas occurs after several sessions.
Although with the help of these methods, the virus external manifestations are completely removed, this is not considered an absolute disposal of infection, but only relative, since a person does not cease to be a virus carrier, and after some period of the wart may occur again.There is no universal method of inoperative treatment for all categories of patients (men, women and children).Only laser removal can be considered an alternative.But when applying it, there is a risk of malignancy (malignancy) papillomas.After the operation, the patient is prescribed by the infusion of one dose of steroid drug, which prevents swelling, and antibiotics are also prescribed to avoid infection of the wound.During therapy, HPV should completely stop the sex life until a full cure, as well as conduct an examination and, if necessary, treatment, a partner.

Treatment at home and folk remedies
In addition to traditional treatment methods, I use others that are officially recognized as medicine and which can be carried out at home:
- Processing of warts with salicylic acid.Every day, warts should be treated with an acid solution (15-20%).This method has one drawback - processing should be done for a rather long time;
- Cream processing.They are lubricated with warts three times a week.But when used, it is possible to feel itching, erosion, redness of the skin is possible;
- Retinoids in the form of a cream.They process warts for - 12 weeks.Its use is also prohibited during pregnancy;
- Injection in the focus of infection once every 7 days, within three to four weeks. Use is prohibited during pregnancy;
- Cauterizing warts, papillomas and destroy pathogenic microbes.The wart should be processed constantly within an hour.Then a break for a week is made and processing is carried out.If papilloma does not disappear, after 14 days another processing is done, and so no more than 4 procedures.It is forbidden to use in senile warts and in pediatrics;
If we talk about treatment with purely folk remedies, then the use of celandine has gained great popularity.Its juice is treated with a wart several times a day.When it darkens, the dark skin is removed and continued to smear further until the wart is completely removed.
Prevention of the disease
The main measures of prevention are considered:
- compliance with personal hygiene in public places;
- compliance with a healthy lifestyle, maintaining immunity;
- one permanent sexual partner, in sexual intercourse with an unverified partner - use a condom;
- sufficient intake of vitamins;
- to lead sex life no earlier than 18 years, when the cervical mucosa is already mature and can protect itself;
- avoid artificial termination of pregnancy and rough sex;
- In time, treat inflammatory diseases.
During vaccination, some side effects in the form of deterioration, fever, redness of the skin at the place of introduction of the vaccine can sometimes be observed.















